Subsistence Agriculture And Population Growth
Since 85 of the population relies on subsistence agriculture population growth affects agricultural land use. Growth in the agriculture sector is two to four times more effective in raising incomes among the poorest compared to.

Macrodemographic Approaches To Population And Subsistence Farming Part Ii The Biodemography Of Subsistence Farming
Ninety per cent of the population are smallscale subsistence farmers.
Subsistence agriculture and population growth. Subsistence agriculture has become extremely important in the face of increasing population growth and dwindling natural resources. 4 persons 3 units of food. We assessed land use change in the Morobe province 33933 km2 using topographic maps of 1975 and Landsat TM images of 1990 and 2000.
The main staple crops grown are banana cassava sweet potato and beans. Between 1975 and 2000 agricultural land use increased by 58 and population grew by 99. With an annual population growth rate of 23 per cent the population is projected to reach 9 million by 2020 and could double by 2050.
In the next 15 years for example the number of people living in African cities is expected to double. 25 years from now. 1 person 1 unit of food.
50 years from now. In this review forms of subsistence agriculture and cha- racteristics and impacts of intensive subsistence agriculture are discussed. 75 years from now.
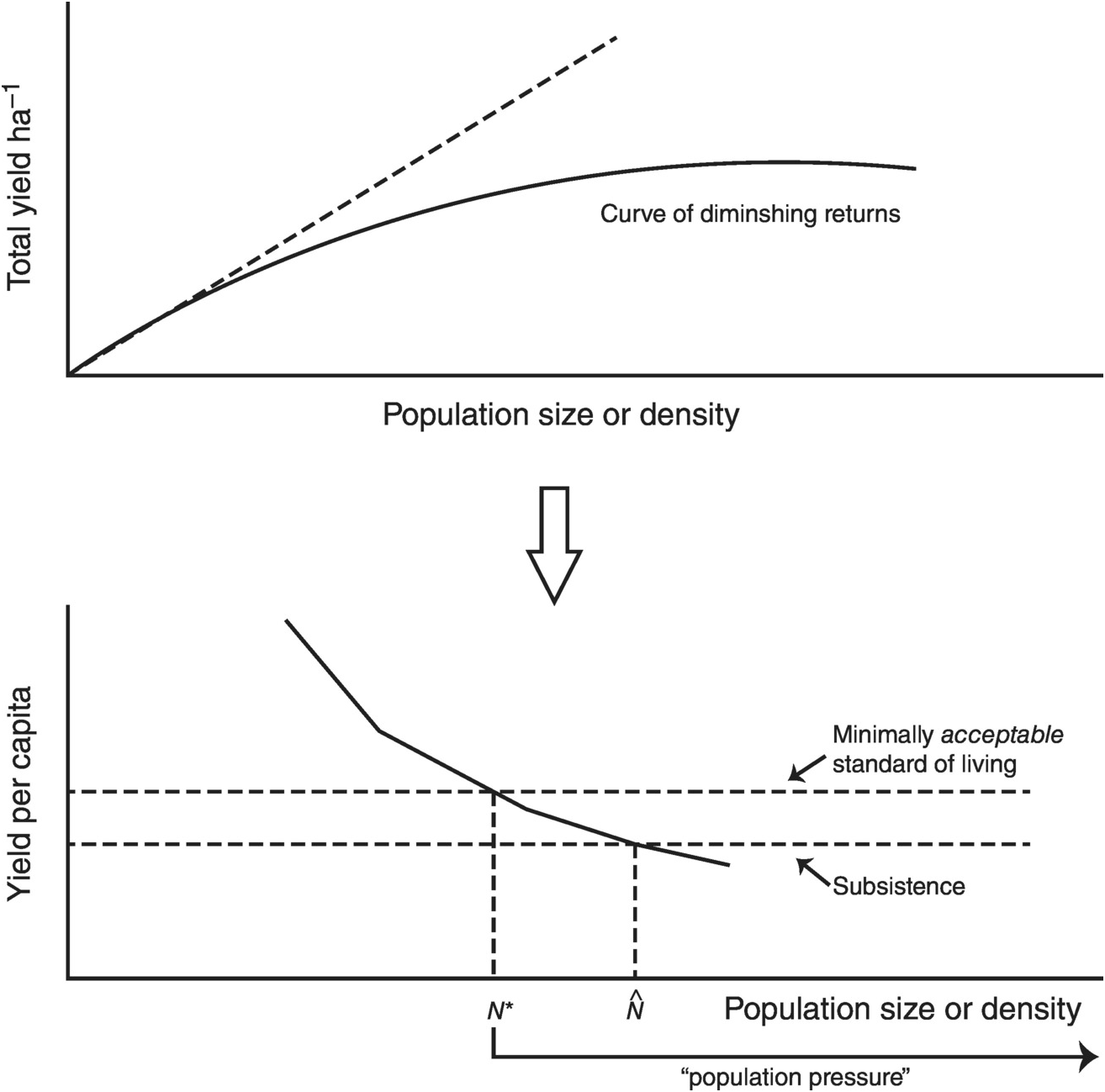
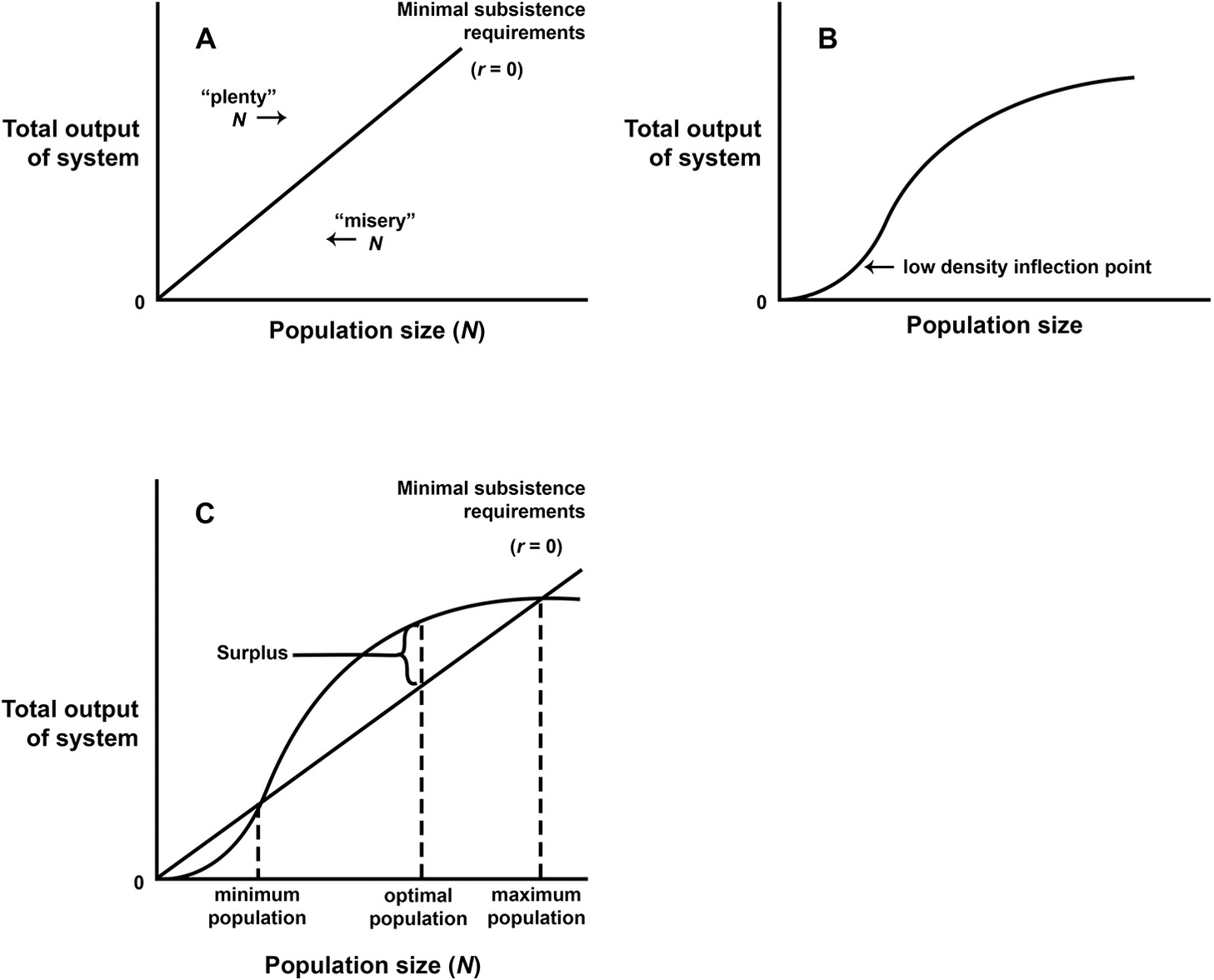
Agricultural development is one of the most powerful tools to end extreme poverty boost shared prosperity and feed a projected 97 billion people by 2050. Ricardo 1817 distinguished between two types of agricultural expansion in response to population growth. Agricultural growth is below the annual population growth rate 32 thus increasing food demand but with low supplyPopulation growth is causing food insecurity land disputes and high numbers of squatters sharecroppers and tenant farmers 4.
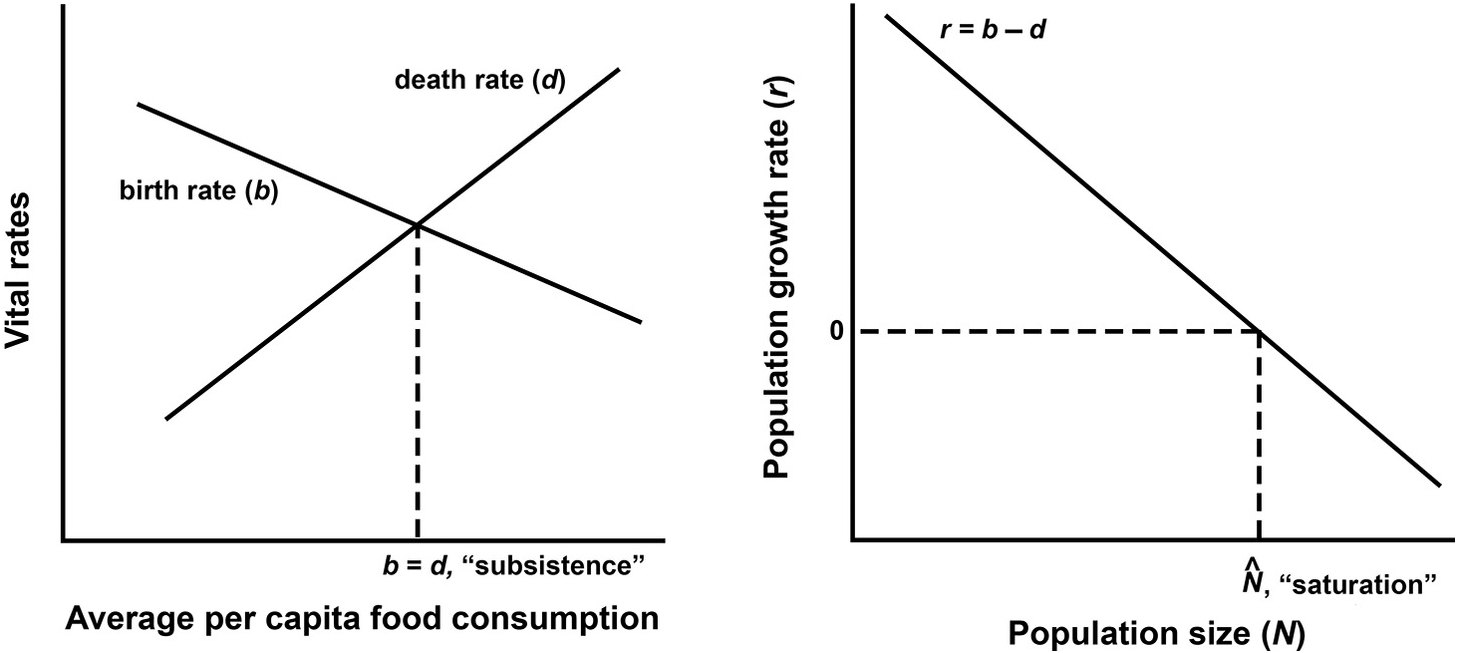
Yet it is precisely these areas where population is growing most rapidly because of higher than average. The same rate of growth measured for populations dwelling in a range of environments and practicing a variety of subsistence strategies suggests that the global climate andor endogenous biological factors not adaptability to local environment or subsistence practices regulated the long-term growth of the human population during most of the Holocene. Of agriculture was linked to accelerated growth of the human population.
Boserup theorized that when population increased in a subsistence agriculturally-based community the level of technology and labor efforts must increase to meet the demands of increased population pressures Boserups basic thesis with respect to population growth in cultures that practiced subsistence agriculture was that. In sub-Saharan Africa subsistence agriculture con- tributes 8-50 of the Gross Domestic Product GDP and employs 40-85 of the rural population Orkin and Njobe 2000. With the advent of agriculture the new technology allowed even higher populations.
This has led to an increase in food production on a small scale leading to rising prices. Efforts to eradicate hunger in rural areas are undermined by low agricultural productivity rapid rates of population growth and explosive urbanization. This subsistence activity on a local level is the greatest threat to the future of the rainforest and the most difficult to address especially in regions with fast-growing populations.
Bananas alone make up almost 30 per cent of the total cultivated area and were 44 per cent of the total value of crop production between 2006 and 2008. And subsistence agriculture Stressors Source Population increase driving fragmentation of landholding. The same rates of prehistoric population growth measured worldwide suggest that the global climate andor biological factors intrinsic to the species and not factors related to the.
8 persons 4 units of food. Land expansion and agricultural intensification are the two contrasted strategies put into practice in Ethiopia. However up to the 18th century population generally grew in line with technology and most of the population remained at subsistence levels.
The report offered other important findings regarding hunger and agriculture. 17 Environmental degradation caused by population poverty and ill-defined and insecure property rights including widespread soil degradation. Eighty-five per cent of the population live in rural areas and seventy-five per cent of households depend on subsistence agriculture.
Malthus proposed that human population was growing exponentially while food production was growing linearly. Below is an example. 90841 Population Growth and LCLU for the Entire Country.
Population could also increase where new land was entered such as the entry of humans into the Americas 12000 years ago. The northern districts of the country are dominated by savanna which supports subsistence agriculture and pastoral activities. One is the extensive margin the expansion into new land which he supposed would yield diminishing returns to labour and capital because the new land was presumed to be more distant or of poorer quality than the land already in use.
Kostov and Lingard 2004. Historically the colonization of rainforest land was encouraged by tropical governments that funded programs to move urban poor out of cities to the unclaimed forest areas. 2 persons 2 units of food.
818 Regionalized and globalized markets and regulatory regimes increasingly concerned with issues of food. People in rural areas have relied more on horticulture and small scale farming to meet their requirements for food and fuel. It is neither an ecological nor an economic environment that can support rapid population growth Codjoe 2007.
Agriculture in terms of crop production and population are growing though the growth trends are different as long as population is steadily growing while production is unexpectedly oscillating.

Ch 8 Food Water And Agriculture Open Geography Education

Subsistence Agriculture An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Agricultural Systems Ap Human Geography Primarily For Direct Consumption By A Local Population Food To Feed Your Family Usually Small Scale And Low Ppt Download
Malthus And Boserup Chapter 5 The Biodemography Of Subsistence Farming

Subsistence Agriculture An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Macrodemographic Approaches To Population And Subsistence Farming Part Ii The Biodemography Of Subsistence Farming
Macrodemographic Approaches To Population And Subsistence Farming Part Ii The Biodemography Of Subsistence Farming

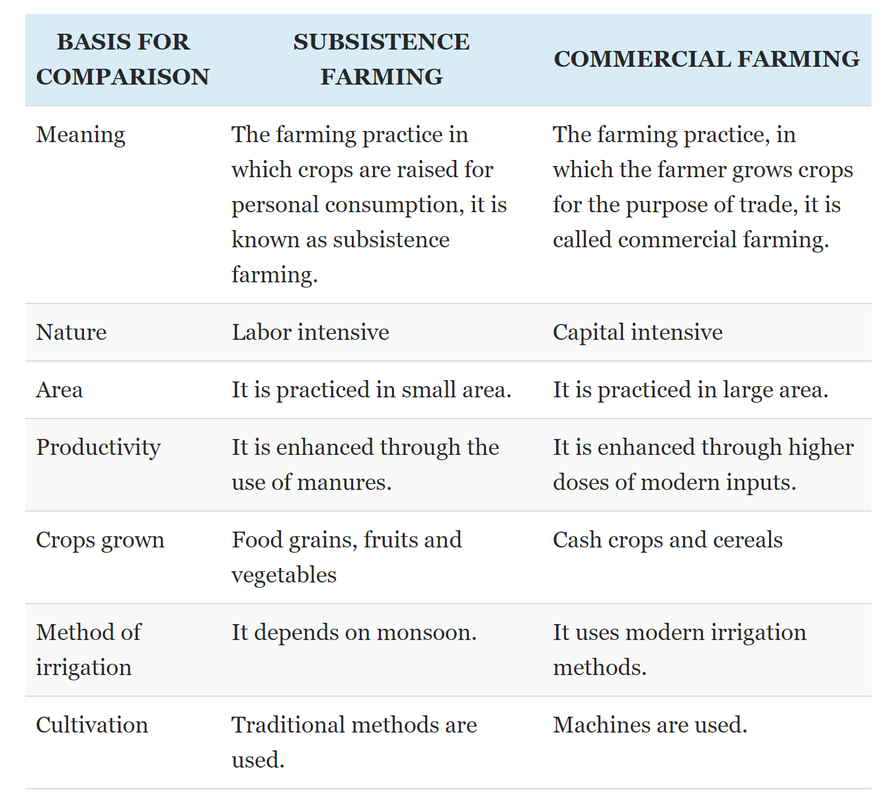
Key Characteristics Of Subsistence And Commercial Farmers Download Table

Macrodemographic Approaches To Population And Subsistence Farming Part Ii The Biodemography Of Subsistence Farming
Food Production The Geographer Online

Subsistence Farming Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Macrodemographic Approaches To Population And Subsistence Farming Part Ii The Biodemography Of Subsistence Farming

Agricultural Regions In Mdc S Ppt Download

Subsistence Agriculture An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Intensive Subsistence Agriculture

Subsistence Farming New World Encyclopedia
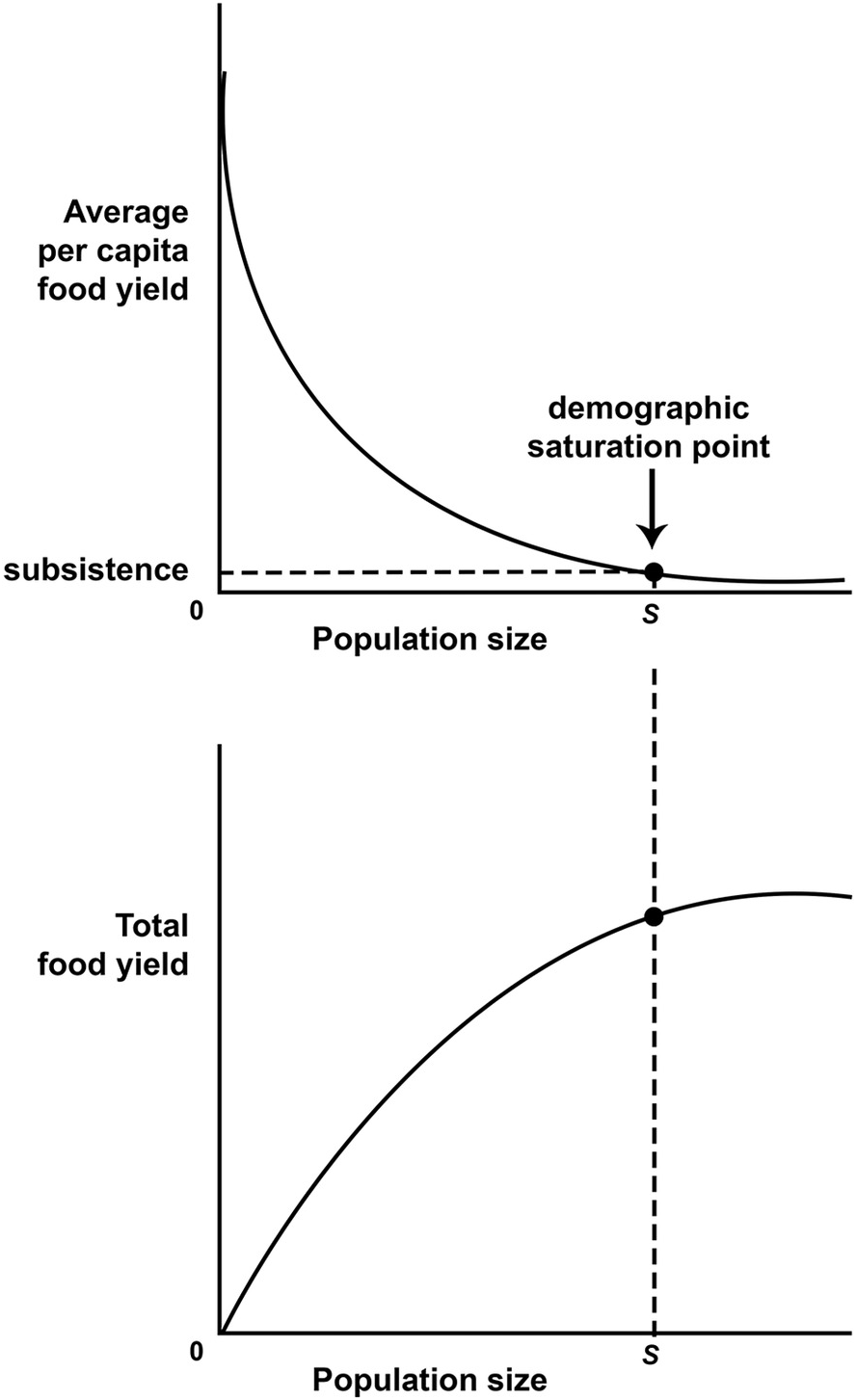
Macrodemographic Approaches To Population And Subsistence Farming Part Ii The Biodemography Of Subsistence Farming
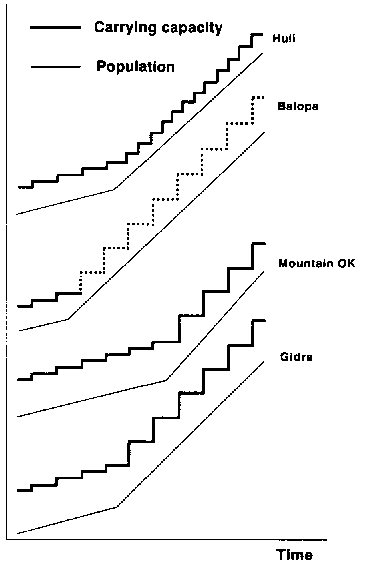
5 Agricultural Sustainability And Food In Papua New Guinea
Post a Comment for "Subsistence Agriculture And Population Growth"