Intensive Farming Examples Of Crops
It relies on reaping high yields with strong and often extreme land exploitation and often extreme inputs. Crops to maximise the amount of food produced.

Intensive Farming And Extensive Farming Difference Between Extensive And Intensive Farming Youtube
Farm and field sizes.
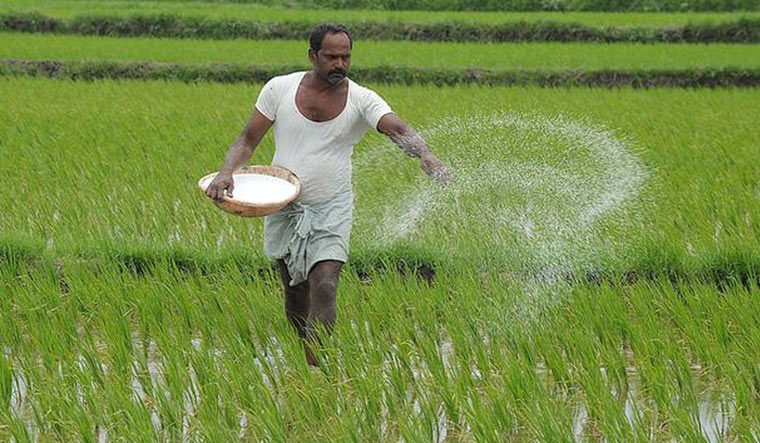

Intensive farming examples of crops. An intensive system reduces the ability of sheep to perform normal grazing and foraging behaviour. The team has been working in northern Western Australia for two. Like wheat corn and barley crops in the North American plains or soy in Argentina it is a.
However advantages never come for free. With industrialization modern intensive farming techniques have been introduced. For example a centre pivot irrigation system or group of centre pivots surrounded by rangelands.
American agriculture may be considered as intensive farming. The plains in the center of the North American continent allow very large field sizes. Cranston in Advances in Sheep Welfare 2017 Intensive farming systems.
Housed or intensive farming systems are clearly different from the environment in which sheep have evolved. One is dominated by wet paddy and the other is dominated by crops other than paddy eg wheat pulses maize millets sorghum kaoling soya-beans tubers and vegetables. Uses machines fertilisers man-power and high-yield.
It moves away from harmful commercial agricultural practices like monoculture annual tilling and other farming methods that lead to soil erosion and the use of pesticides. It results in much more food being produced per acre compared to other subsistence patterns. In countries like China India Bangladesh etc.
Although the animal welfare implications of a lack of diet selection and grazing preference. Intensive farming is an agricultural method of increasing the crop yield by heavy use of chemicals such as fertilizers pesticides etc. Aerial photo of pastures under centre pivot irrigation.
The main benefits of intensive farming include sufficient food supplies at affordable prices. Examples of intensive agriculture Massive monocultures. Optimal use of these materials and machines produces significantly greater crop yields per unit of land than extensive agriculture which uses little capital or labour.
Monocropping is a defining feature of intensive plant agriculture. Compost in biointensive farming can be obtained by carbon farming. Intensive Agriculture Intensive agriculture is the primary subsistence pattern of large-scale populous societies.
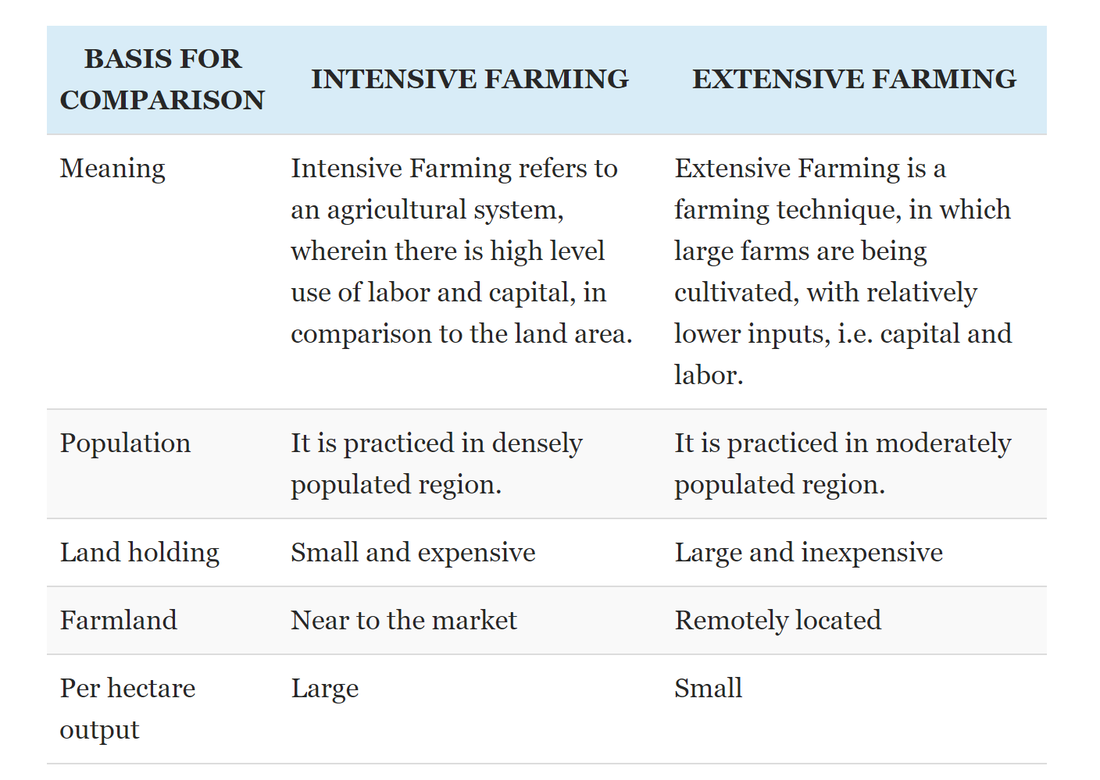
On the other extreme extensive farming is a farming method wherein acres of land are being farmed with lower inputs ie. Intensive agriculture is the most typical method of soil cultivation and the key source of food worldwide. To enhance productivity maximum labourers are engaged in agriculture and production process become labour intensive.
Labour and investment in comparison to the land. Large areas of land are planted with a single species such as wheat corn or soy with the latter two used heavily in. Beginning about 5000 years ago the development of intensive farming methods became necessary as the human population grew in some major river valleys to levels beyond the carrying.
The techniques help in production of the highest yield at the lowest possible cost. Intensive farming is generally practiced in densely populated countries. Pastures under centre pivot irrigation.
There are two types of the intensive subsistence agriculture. Carbon farming is based on cultivating crops which have high amounts. Farmers growing arable crops often specialise in growing only one crop to.
Intensive agriculture in a potato field in Fort Fairfield Maine US. Pre-mordern era of intensive farming included terracing rice paddies as well as aquacultue aquafarming. It refers to small areas of intensive agriculture in an extensive rangelands setting.
Broadacre grain crops dominate with cattle grazing in regions with insufficient rainfall. Permaculture farming is a method of agriculture thats based on sustainability. Some of the types of intensive farming are as follows.
Due to over-emphasis on agricultural sector and lack of diversified economic occupationeven huge number of labour are disguisedly employed in. It is called greenhouse to closed places and controlled climatic conditions. As a result a farm using intensive agriculture will require less land than.
Permaculture can be defined as a permanent cultural system that is based on observing nature. The system of bio-intensive farming is based upon certain componentsMethods which include.
Food Production The Geographer Online

The Pros And Cons Of Intensive Farming
/thinkstockphotos-151513663-5bfc353e4cedfd0026c2e3a8.jpg)
How To Invest In Farming Without Owning A Farm

Micro Farming Little Farms With Big Profits Farmers Weekly

Advantages And Disadvantages Of Intensive Farming
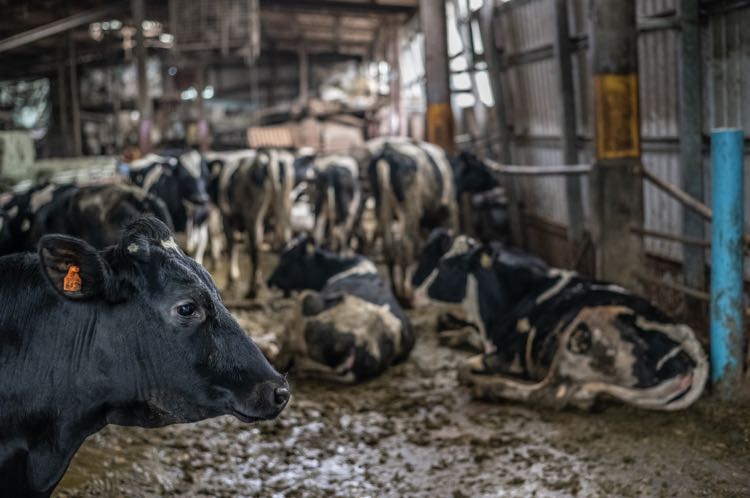

Intensive Agriculture Impact On Humans Animals And The Planet

21 Of The Best Small Scale Farming Ideas Grocycle

Difference Between Intensive And Extensive Farming Farming Base

Intensive Agriculture Impact On Humans Animals And The Planet

Monoculture Do Intensive Farming And Gmos Really Threaten Biodiversity Genetic Literacy Project
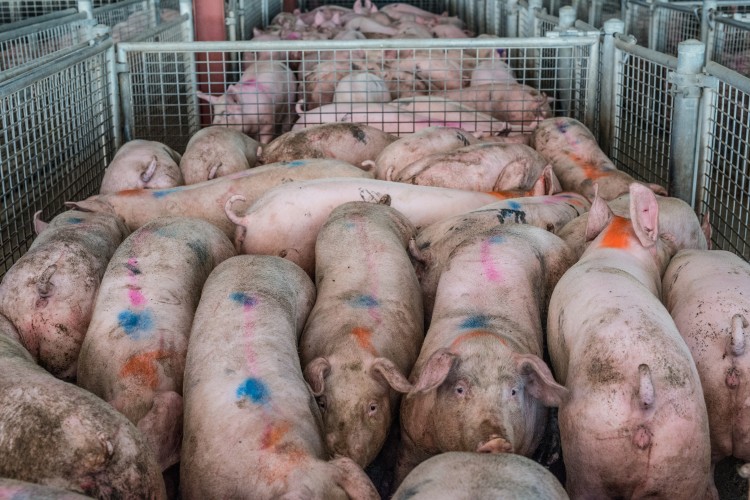

Intensive Agriculture Impact On Humans Animals And The Planet

How Small Farms Can Sustainably Feed The Future By Louisa Chalmer Age Of Awareness Medium

Advantages And Disadvantages Of Intensive Fruit Farming Greentumble

Intensive Farming More Environment Friendly Than Organic Methods Study The Week

Advantages And Disadvantages Of Intensive Farming
Intensive Agriculture Cultural Anthropology

10 Benefits Of Crop Rotation In Agriculture Greentumble

Intensive Farming Ecologically Sustainable Euractiv Com

Post a Comment for "Intensive Farming Examples Of Crops"